激活函数(Activation Function)
为了让神经网络能够学习复杂的决策边界(decision boundary),我们在其一些层应用一个非线性激活函数。最常用的函数包括 sigmoid、tanh、ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit 线性修正单元) 以及这些函数的变体。
由于激活函数可用来限制神经元的输入输出振幅,它也称为压制函数,因为它的输出信号压制(限制)到允许范围之内的一定值。
- affine transformation $a = b+Wx$, elementwise

Why use?
Activation functions for the hidden units are needed to introduce nonlinearity into the network. Without nonlinearity, hidden units would not make nets more powerful than just plain perceptrons (which do not have any hidden units, just input and output units). The reason is that a linear function of linear functions is again a linear function. However, it is the nonlinearity (i.e, the capability to represent nonlinear functions) that makes multilayer networks so powerful. Almost any nonlinear function does the job, except for polynomials.
For backpropagation learning, the activation function must be differentiable, and it helps if the function is bounded; the sigmoidal functions such as logistic and tanh and the Gaussian function are the most common choices. Functions such as tanh or arctan that produce both positive and negative values tend to yield faster training than functions that produce only positive values such as logistic, because of better numerical conditioning (see ftp://ftp.sas.com/pub/neural/illcond/illcond.html).
which one to choose?
For hidden units, sigmoid activation functions are usually preferable to threshold activation functions. Networks with threshold units are difficult to train because the error function is stepwise constant, hence the gradient either does not exist or is zero, making it impossible to use backprop or more efficient gradient-based training methods. Even for training methods that do not use gradients--such as simulated annealing and genetic algorithms--sigmoid units are easier to train than threshold units. With sigmoid units, a small change in the weights will usually produce a change in the outputs, which makes it possible to tell whether that change in the weights is good or bad. With threshold units, a small change in the weights will often produce no change in the outputs.
For the output units, you should choose an activation function suited to the distribution of the target values:
- For binary (0/1) targets, the logistic function is an excellent choice (Jordan, 1995).
- For categorical targets using 1-of-C coding, the softmax activation function is the logical extension of the logistic function.
- For continuous-valued targets with a bounded range, the logistic and tanh functions can be used, provided you either scale the outputs to the range of the targets or scale the targets to the range of the output activation function ("scaling" means multiplying by and adding appropriate constants).
- If the target values are positive but have no known upper bound, you can use an exponential output activation function, but beware of overflow.
- For continuous-valued targets with no known bounds, use the identity or "linear" activation function (which amounts to no activation function) unless you have a very good reason to do otherwise.
发展历史
线性函数
恒等函数(Identity)或线性激活(Linear activation)函数是最简单的激活函数。输出和输入成比例。线性激活函数的问题在于,它的导数是常数,梯度也是常数,梯度下降无法工作。
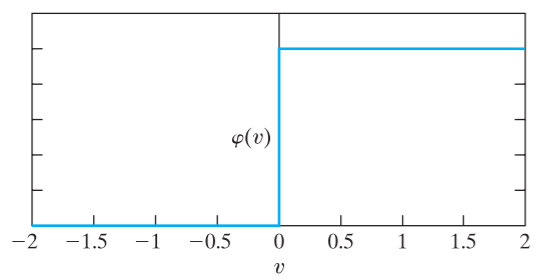
阶跃函数(step function)
sigmoid函数/Logistic函数
逻辑函数或逻辑曲线是一种常见的S形函数,它是皮埃尔·弗朗索瓦·韦吕勒在1844或1845年在研究它与人口增长的关系时命名的。广义Logistic曲线可以模仿一些情况人口增长(P)的S形曲线。起初阶段大致是指数增长;然后随着开始变得饱和,增加变慢;最后,达到成熟时增加停止。
一个简单的Logistic函数可用下式表示:
Logistic函数也称逻辑激活函数(Logistic activation function)可以看作是对阶跃函数的平滑化拟合。
- 计算sigmoid函数的导数非常简单。$f'(x)=f(x)(1-f(x))$
- 最常用于二元分类问题。
- 梯度消失问题。在一定epoch数目之后,网络拒绝学习,或非常缓慢地学习,因为输入(X)导致输出(Y)中非常小的改动。这一函数更容易碰到后续层的饱和问题,导致训练变得困难。
![此处输入图片的描述][9]
非线性且处处可微
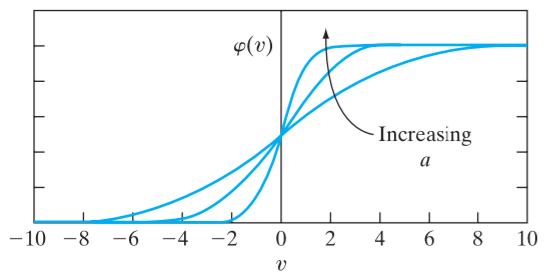
tanh函数
- motivation: to compose simple transformations in order to obtain highly non-linear ones
- (MLPs compose affine transformations and element-wise non-linearities)
hyperbolic tangent activation functions:

- the input of the neural net:
- the output of the k-th hidden layer:
ReLU
线性修正单元(Rectified Linear Unit)。ReLU 常在深度神经网络中被用作激活函数。它们的定义是:
ReLU 相对于 tanh 等函数的优势包括它们往往很稀疏(它们的激活值可以很容易设置为 0),而且它们受到梯度消失问题的影响也更小。ReLU 主要被用在卷积神经网络中用作激活函数。ReLU 存在几种变体,如Leaky ReLUs、Parametric ReLU (PReLU) 或更为流畅的 softplus近似。
论文:
- 深入研究修正器(Rectifiers):在 ImageNet 分类上超越人类水平的性能(Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification)
- 修正非线性改进神经网络声学模型(Rectifier Nonlinearities Improve Neural Network Acoustic Models )
- 论文:线性修正单元改进受限玻尔兹曼机(Rectified Linear Units Improve Restricted Boltzmann Machines )