标准化
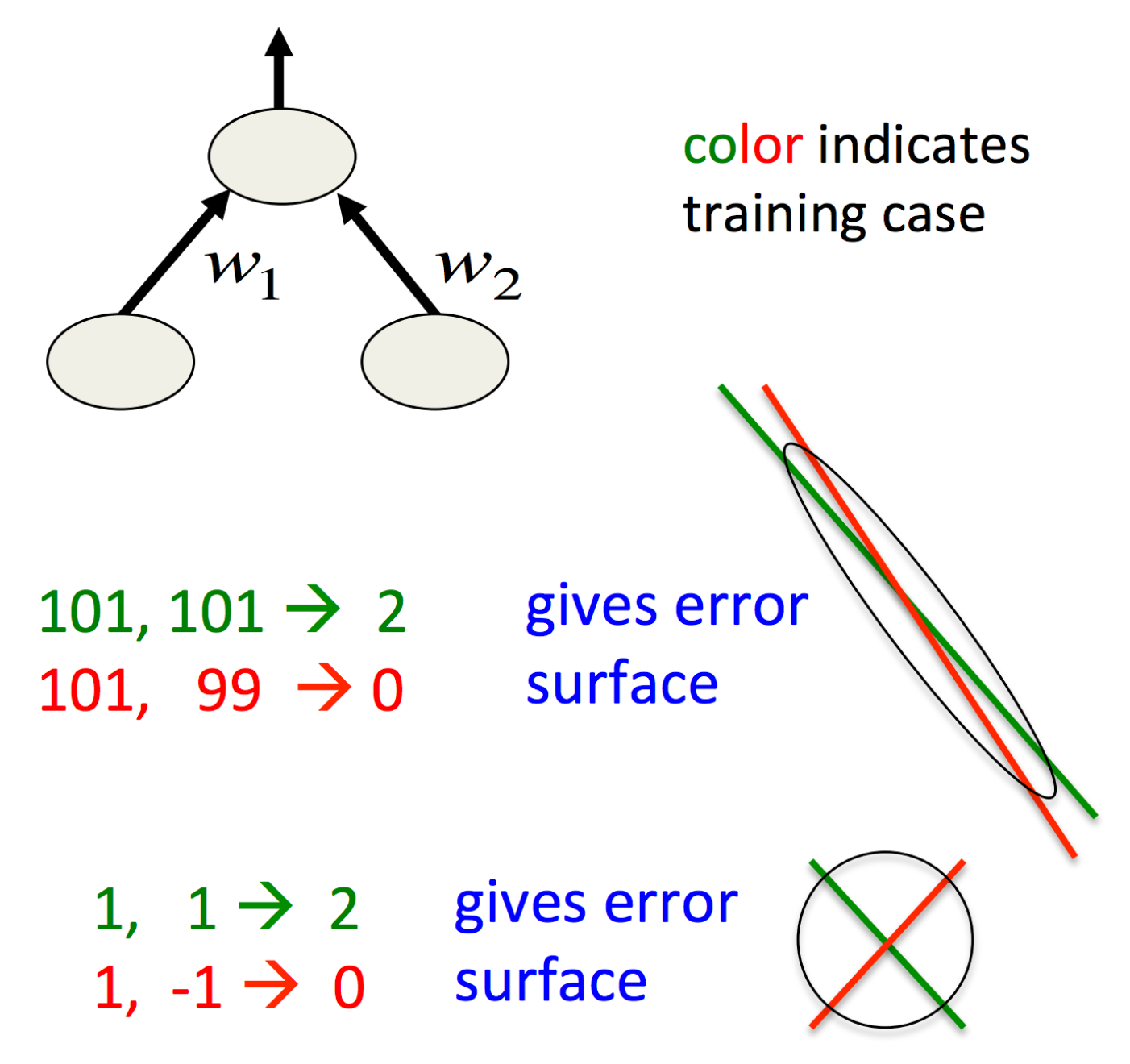
NNML第六周印象最深的是从误差曲面的角度理解数据预处理,甚至是PCA。如果误差曲面是椭圆的话,最速下降方向往往不指向最小值,这样一来,很可能在偏离很大的方向走了很大一步,这种情况下较大的学习率还会导致震荡。 在使用最速下降时,对输入进行transfer和scale:
- transfer:训练集的输入向量均值为0
- scale:
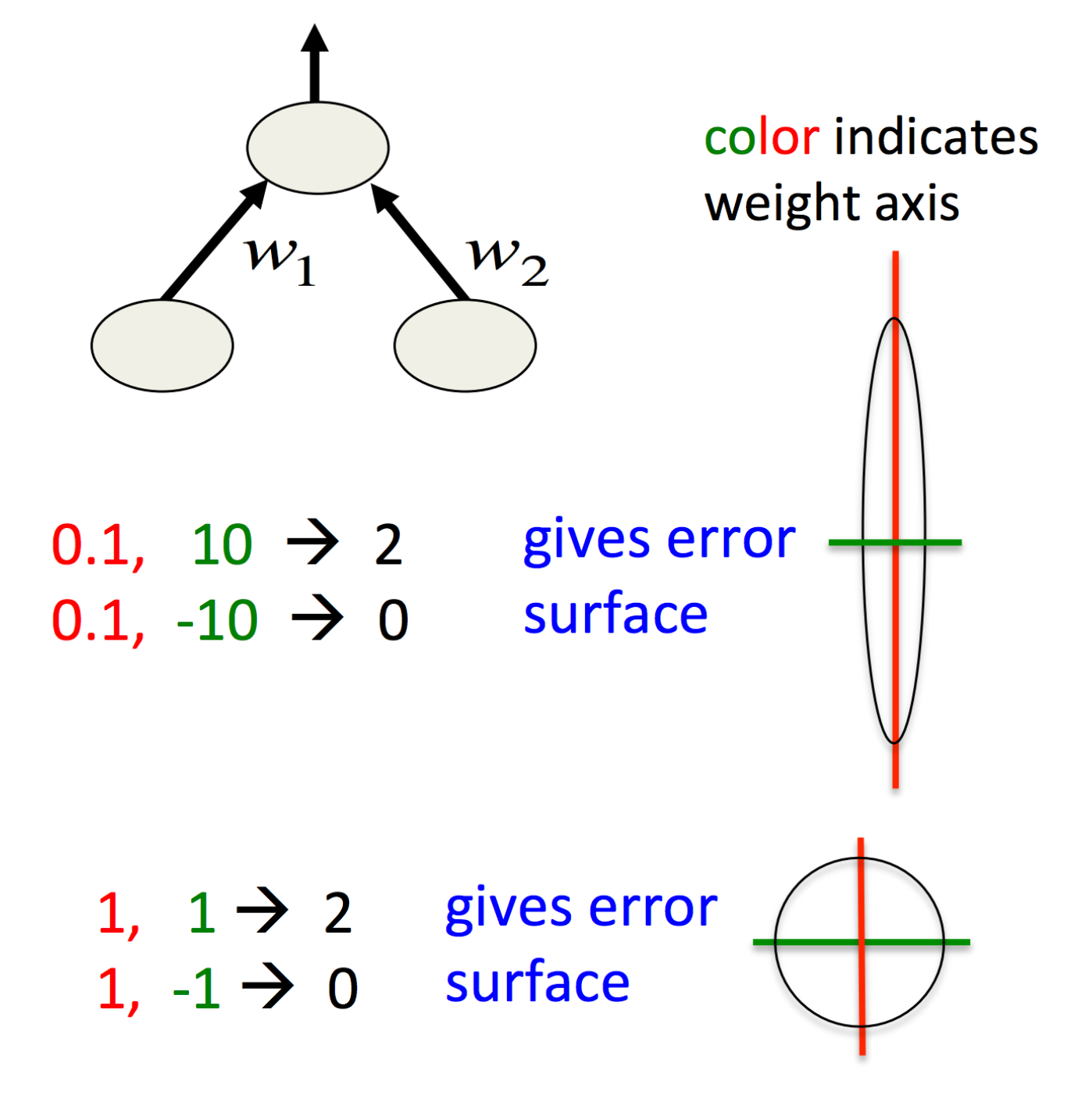
- Decorrelate the input(PCA):去掉特征值较小的主成分,剩下的除以对应的特征值的平方根,对于线性单元来说,这样就把椭圆的误差曲面转变成了圆形。而对于圆形的误差曲面,梯度下降方向指向最小值。
分批标准化(BN:Batch Normalization)
分批标准化是一种按小批量的方式标准化层输入的技术。它能加速训练过程,允许使用更高的学习率,还可用作规范器(regularizer)。人们发现,分批标准化在卷积和前馈神经网络中应用时非常高效,但尚未被成功应用到循环神经网络上。
论文:分批标准化:通过减少内部协变量位移(Covariate Shift)加速深度网络训练(Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift)
论文:使用分批标准化的循环神经网络(Batch Normalized Recurrent Neural Networks)
Two techniques to help with this are feature scaling and mean normalization. Feature scaling involves dividing the input values by the range (i.e. the maximum value minus the minimum value) of the input variable, resulting in a new range of just 1. Mean normalization involves subtracting the average value for an input variable from the values for that input variable resulting in a new average value for the input variable of just zero. To implement both of these techniques, adjust your input values as shown in this formula:
adaBN:Batch normalization和Instance normalization的对比
Simplified Whitening
The mean and variance of the pixels across the batch is calculated and then centered and scaled respectively. It’s said that it speeds up convergence.
Local Contrast Normalization
def LocalContrastNorm(image,radius=9):
"""
image: torch.Tensor , .shape => (1,channels,height,width)
radius: Gaussian filter size (int), odd
"""
if radius%2 == 0:
radius += 1
def get_gaussian_filter(kernel_shape):
x = np.zeros(kernel_shape, dtype='float64')
def gauss(x, y, sigma=2.0):
Z = 2 * np.pi * sigma ** 2
return 1. / Z * np.exp(-(x ** 2 + y ** 2) / (2. * sigma ** 2))
mid = np.floor(kernel_shape[-1] / 2.)
for kernel_idx in range(0, kernel_shape[1]):
for i in range(0, kernel_shape[2]):
for j in range(0, kernel_shape[3]):
x[0, kernel_idx, i, j] = gauss(i - mid, j - mid)
return x / np.sum(x)
n,c,h,w = image.shape[0],image.shape[1],image.shape[2],image.shape[3]
gaussian_filter = Variable(torch.Tensor(get_gaussian_filter((1,c,radius,radius))))
filtered_out = F.conv2d(image,gaussian_filter,padding=radius-1)
mid = int(np.floor(gaussian_filter.shape[2] / 2.))
### Subtractive Normalization
centered_image = image - filtered_out[:,:,mid:-mid,mid:-mid]
## Variance Calc
sum_sqr_image = F.conv2d(centered_image.pow(2),gaussian_filter,padding=radius-1)
s_deviation = sum_sqr_image[:,:,mid:-mid,mid:-mid].sqrt()
per_img_mean = s_deviation.mean()
## Divisive Normalization
divisor = np.maximum(per_img_mean.data.numpy(),s_deviation.data.numpy())
divisor = np.maximum(divisor, 1e-4)
new_image = centered_image.data / torch.FloatTensor(divisor)
return new_image