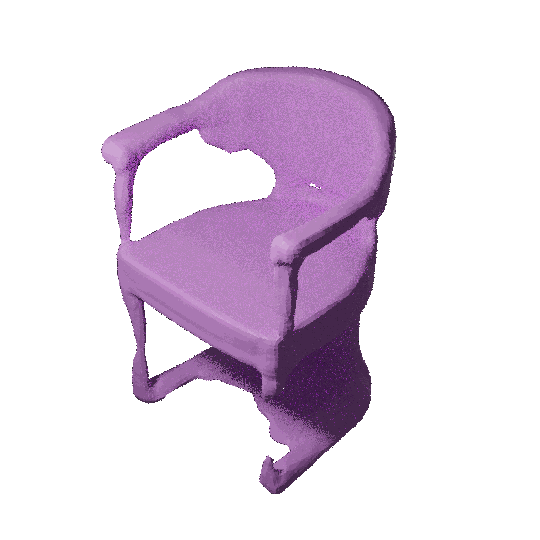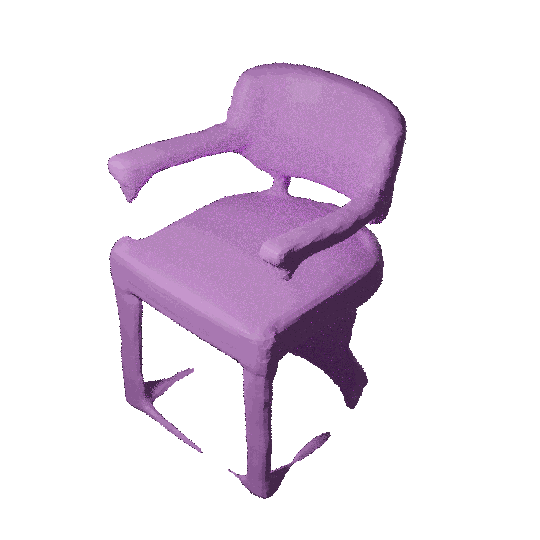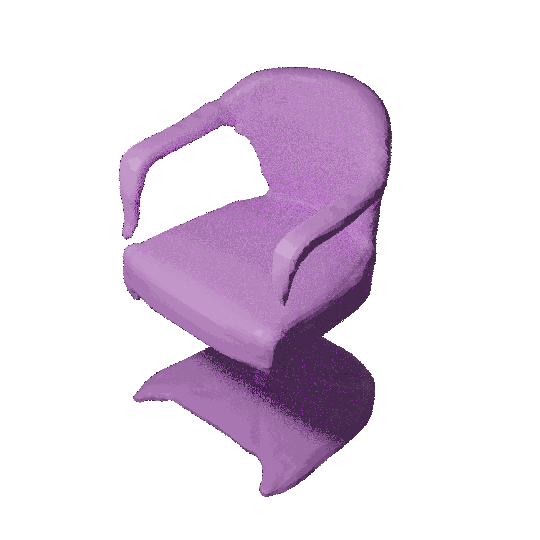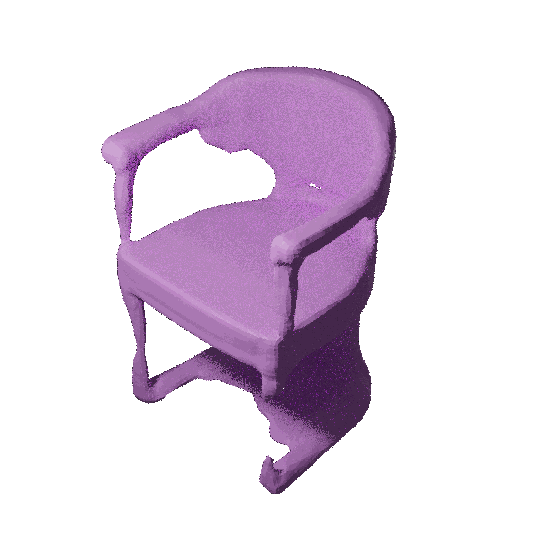3D VR Sketch Guided 3D Shape Prototyping and Exploration
Ling Luo, Pinaki Nath Chowdhury, Tao Xiang, and 2 more authors
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023
3D shape modeling is labor-intensive and time-consuming and requires years of expertise. Recently, 2D sketches and text inputs were considered as conditional modalities to 3D shape generation networks to facilitate 3D shape modeling. However, text does not contain enough fine-grained information and is more suitable to describe a category or appearance rather than geometry, while 2D sketches are ambiguous, and depicting complex 3D shapes in 2D again requires extensive practice. Instead, we explore virtual reality sketches that are drawn directly in 3D. We assume that the sketches are created by novices, without any art training, and aim to reconstruct physically-plausible 3D shapes. Since such sketches are potentially ambiguous, we tackle the problem of the generation of multiple 3D shapes that follow the input sketch structure. Limited in the size of the training data, we carefully design our method, training the model step-by-step and leveraging multi-modal 3D shape representation. To guarantee the plausibility of generated 3D shapes we leverage the normalizing flow that models the distribution of the latent space of 3D shapes. To encourage the fidelity of the generated 3D models to an input sketch, we propose a dedicated loss that we deploy at different stages of the training process.